
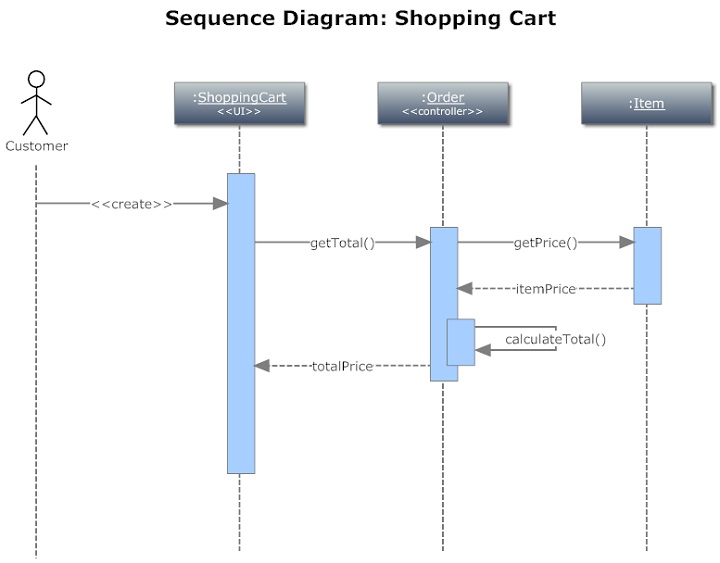
Sequence diagram example simple registration#
But before that, objects and classes will be displayed in a registration process system. The functionality of the entire system is influenced by the sequence of messages exchanged amongst its objects. The arrowhead used to show this type of message is a simple line arrow with a dark-colored tip, as shown in the diagram above.Įxample 2: Registration Process Sequence Diagram Source: EdrawMax An asynchronous message passed between the customer, login screen, and security management is employed when the message dialer does not wait for the receiver to process the message and make a response before sending other messages to other already defined objects within the proposed system. They use it to illustrate how the different parts of a system will interact with each other and sequential order to achieve a desirable outcome.Ī case in point to help you visualize and fully grasp the UML sequence diagram is as follows. In more than half of the instances of using the sequence diagram, IT developers will more times than not be using them. Example 5: Web User UML Sequence DiagramĮxample 1: Transaction System Sequence Diagram Source: EdrawMax.Example 4: Website UML Sequence Diagram.Example 3: Login Student System Sequence Diagram.Example 2: Registration Process Sequence Diagram.Example 1: Transaction System Sequence Diagram.For example, an employee is dependent on the organization. Change in one class will create change in another class. For example, if an organization closes, all employees will have to leave.ĭependency shows that one class depends on another. In composition, a class is strongly connected to another class that it will stop functioning without it. The aggregation has another special type, called composition. For example, if an employee does not come, the organization will remain there. In aggregation, 2 classes have a whole-part relationship. If 100 people work at an organization, then the attribute has multiplied 100 times. The multiplicity factor in association represents how many times an attribute is multiplied. The association between a student and school is “studies”. Checking, Savings, and Credit Accounts are generalized by AccountĪssociation shows a static relationship between two entities. The class diagram allows a subclass to inherit from multiple superclasses but it can’t be used to model interface implementation. Generalizations are often known as Inheritance because it links a subclass to its superclass. There are three main types of relationships here: To create a class diagram, the next step is building relationships.
You don’t need to show operations that are similar to attributes because one can already deduce that from the information. They correspond to the methods of a class. Operations are processes that a class knows to carry out. Attributes must be meaningful and are usually used with the visibility factor that describes the accessibility of an attribute. You can simply add new attributes or derive new attributes from already listed attributes. Moreover, an abstract class should be written in italics.Īttributes are written in the middle compartment and list down all the properties of the object being modeled. It should be written in bold in the top compartment and start with a capital letter. The class name is important for graphical representation.

The rectangle is divided into three compartments with the topmost being Class Name, then Attributes in the middle, and Operations in the bottom. There are three major parts of a class diagram as shown in the image below:Ī single rectangle is used to represent the class as shown above.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
